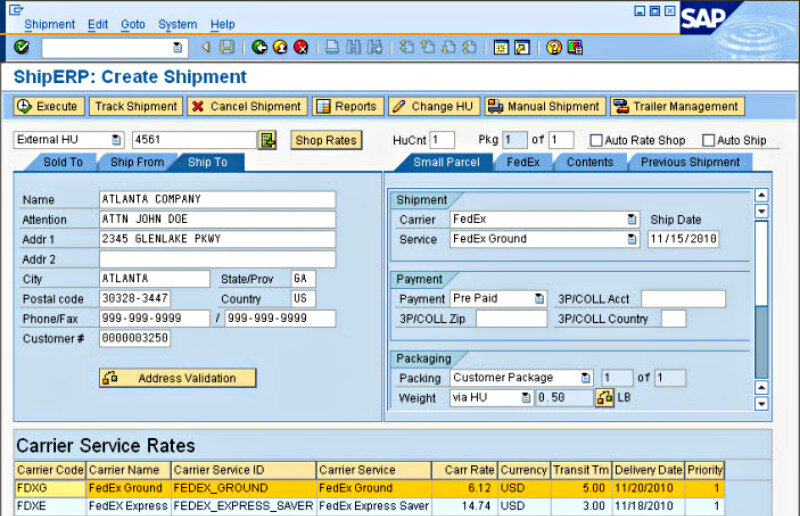
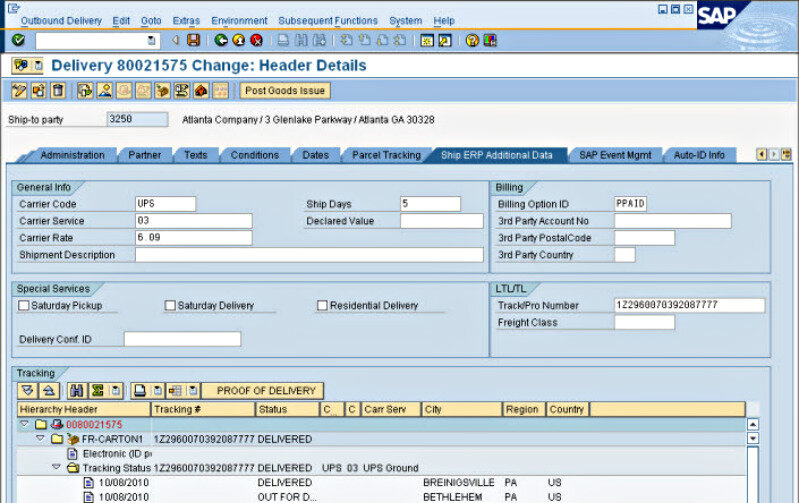
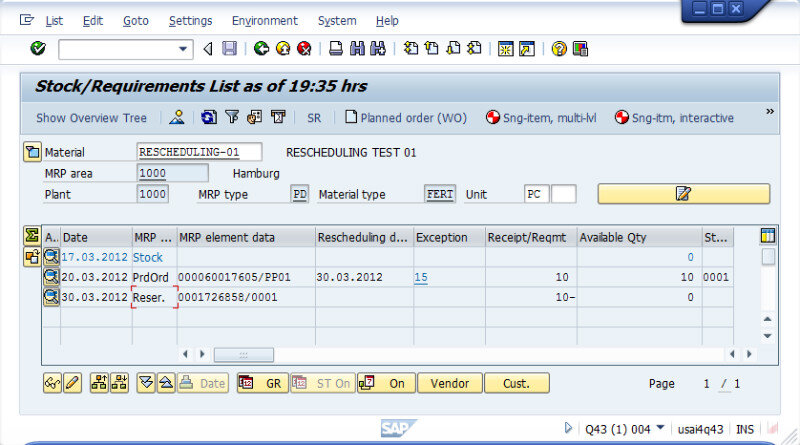
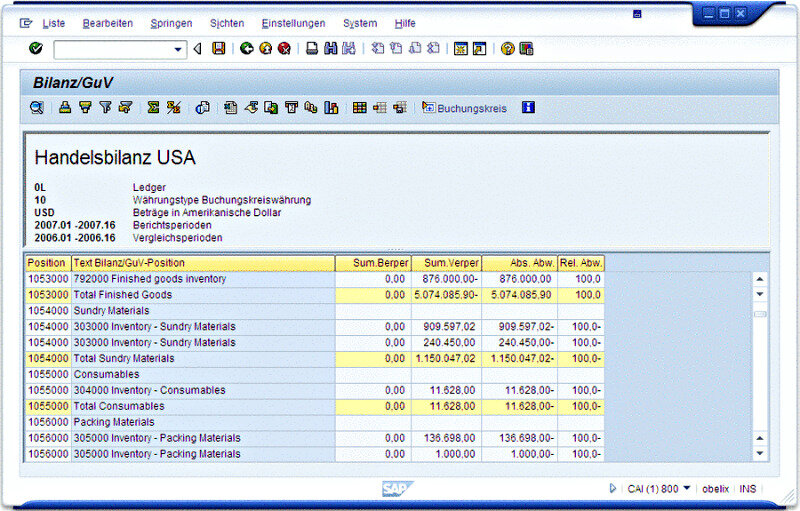
What is SAP ERP?
SAP ERP is an integrated on‑premises software system developed by SAP SE that unifies a company’s key business functions( finance, sales, manufacturing, HR, logistics, and more) within a single central database.
Each SAP ERP module (for example, Finance & Controlling, Sales & Distribution, Materials Management, or Human Capital Management) addresses a core business area. Modules share data in real time, so information flows across the organization without duplicate entry.
The system supports 39 languages and covers the entire manufacturing and logistics lifecycle. Core modules include standard ERP features as well as HR and finance. Customers can apply regular upgrades selectively to various business functions.
Designed for a wide range of industries, SAP ERP serves process manufacturers in pharmaceuticals, insurance firms, wholesale distributors, higher education institutions, and more.
SAP markets SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) as its traditional ERP solution for medium and large enterprises. The latest on‑premises release was SAP ERP 6.0 (with Enhancement Pack 8) in 2006.
SAP ERP end-of-support
SAP ERP is now considered legacy software; SAP plans end‑of‑support for SAP ERP 6.0 by December 31, 2027, after which customers will receive only maintenance fixes. Organizations should plan migration to SAP S/4HANA well before that deadline.
Modules and functionality
SAP ERP’s strength lies in its comprehensive suite of optional modules. Companies select only the modules they need, making the system scalable from dozens to hundreds of integrated applications.
Core modules include:
- Financial accounting & controlling (FICO): handles general ledger, accounts payable/receivable, budgeting, and financial reporting.
- Sales & distribution (SD): Manages orders, pricing, shipping, billing, and customer relationships.
- Materials management (MM): covers purchasing, inventory management, and procurement processes.
- Production planning (PP): Supports manufacturing schedules, capacity planning, and shop-floor execution.
- Quality management (QM): Tracks quality control and compliance processes.
- Plant maintenance (PM): Schedules and records maintenance for equipment and facilities.
- Project system (PS): Manages project planning, costs, and timelines.
- Customer service (CS): Supports service orders and customer support.
- Human capital management (HCM): Manages payroll, personnel administration, time tracking, and employee development.
The software uses a standard SAP GUI interface and three‑tier architecture (presentation, application, database). SAP’s proprietary ABAP/4 programming language underpins the system, enabling deep customization and extensions.
Flexibility and deployment options
SAP ERP runs on a variety of operating systems including Windows, Linux, and UNIX.
You can deploy on‑premises or in the cloud. SAP ERP integrates with SAP Cloud Platform, enabling hybrid scenarios and third‑party cloud services.
Users access SAP ERP via a web interface (SAP Fiori) which provides a modern, role‑based experience on desktops, smartphones, and tablets.
SAP ERP interface
The platform offers:
- SAP GUI: The classic desktop client for power users.
- SAP Fiori: A responsive, tile‑based web interface optimized for mobile and desktop.
- OData/Open API: Enables custom UI development with RESTful services.
Frequently asked questions
Is SAP ERP a SaaS?
SAP ERP Central Component (ECC) is an on‑premises system. SAP does not offer ECC as a true SaaS solution, but you can host it in private or public clouds via partners. Its successor, SAP S/4HANA Cloud, provides a multi‑tenant SaaS option.
What is the difference between SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA?
The primary difference between SAP ERP and SAP S/4HANA lies in the system architecture and deployment flexibility.
- Architecture: SAP ERP (ECC) uses traditional relational databases; SAP S/4HANA runs on the in‑memory SAP HANA database for faster transaction processing.
- Deployment: ECC is on‑premises (with partner‑hosted cloud options); S/4HANA offers on‑premises, private cloud, public cloud, and hybrid editions.
- Analytics & AI: S/4HANA embeds advanced analytics, machine learning, and predictive planning, giving real‑time insights.
How much does SAP cost?
SAP ERP pricing varies widely based on deployment, user count, modules, and customization. Typical cost components include:
- Software licensing
- Customization and implementation (this can vary massively depending on complexity, whether or not an implementation partner is used or not etc.)
- Maintenance and support (an annual fee of around 15-20% of the software licensing fee).
For a better idea of ERP pricing, click the 'price' button above.
Software features
- Billing
- Business Intelligence/Analytics
- Costing
- CRM
- Customer Service
- Product Design
- Financials & Accounting
- HR
- Inventory Management
- Order Management
- Planning & Scheduling
- Project Management
- Purchasing
- Quality Control
- Sales
- Shipping & Distribution
- Supply Chain Management
- Warehouse Management
- Asset Management
- Document Management
Quick spec
Product details
Customer Suitability
- Enterprise (1000+ Employees)
- Medium Size (251-1000 Employees)
- Small Business (1-250 Employees)
Additional Product Info
- Multi Language
- Multi Currency
- Customizable
System Hosting
- Cloud
- Installed on Premise
Your comparison
Download more information
SAP ERP
Download exclusive feature and pricing data with your free extended profile of SAP ERP .
DownloadWork for SAP?
Update the SAP ERP profile with your latest feature, screenshots and pricing to reach more buyers. Click the link below to get started.
Update this profileRelated articles
-

A complete ERP RFP template & guide (includes free template)
All you need to know construct a foolproof ERP RFP, including a customizable template
-

CMMC Compliance: What Aerospace and Defense Manufacturers Need to Know
Key insights on CMMC compliance, deadlines, and securing DoD contracts with CMMC 2.0 certificatio...
-

Top 10 ERP selection criteria (including checklist)
The most important ERP selection criteria you should keep in mind during your selection process.
SAP ERP
Pricing Guide

SAP ERP
Download your pricing guide by completing the form below.
SAP ERP
Price Quote

SAP ERP
Complete the form below to access a video demo of this software.
Quickly Compare with Similar ERP Systems
Other Users often Compare these Four Solutions
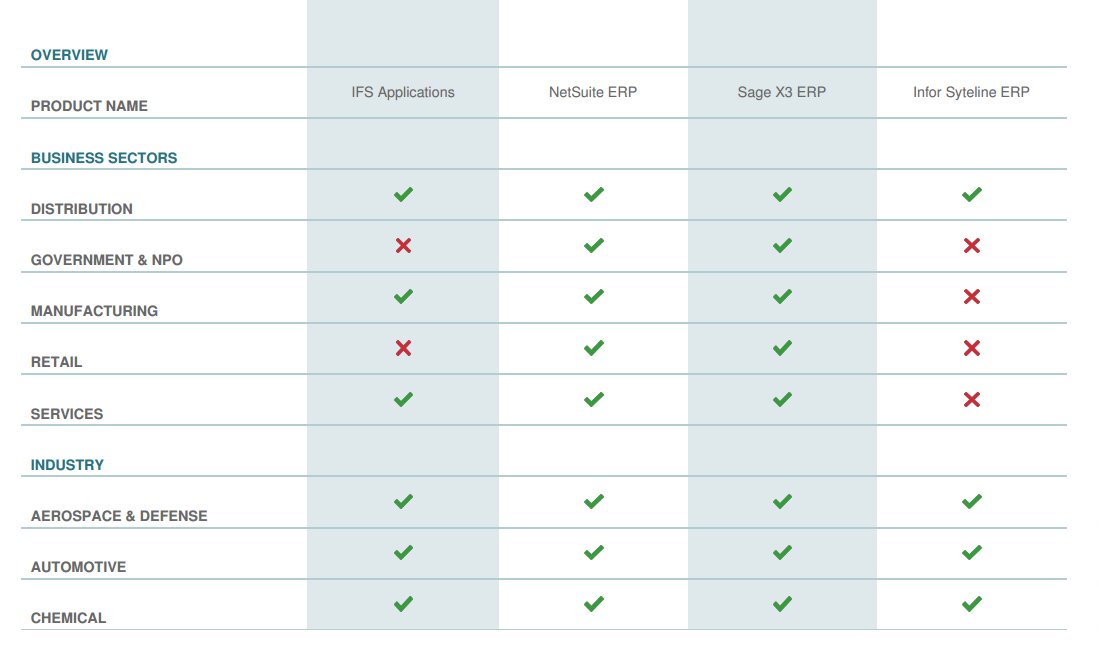
Get Your ERP Software Comparison
Download your bespoke report in a single pdf.
SAP ERP
Extended Software Profile

SAP ERP
Get your extended software profile by completing the form below.
SAP ERP
Extended Software Profile